When writing JavaScript code, you might want to delay the execution of a function. Learn how to use setTimeout and setInterval to schedule functions in the future
当写js代码的时候,你可能需要延迟执行某个方法。现在来学习下如果用setTimeout和setInterval来定时执行。
setTimeout(callback, timeout)
setTimeout接受2个参数,第一个callback代表你将要延迟执行的方法,第二个参数代表你将要延迟的时间,以milliseconds为单位。
1 | setTimeout(() => { |
下面的句法定义了新的function,你可以直接调用这个方法,或者把它当成一个参数传递给setTimeout延时执行1
2
3
4
5
6const myFunction = (firstParam, secondParam) => {
// do something
}
// runs after 2 seconds
setTimeout(myFunction, 2000, firstParam, secondParam)
setTimeout方法返回一个timer id,大部分情况下用不到它,但是可以存储它,以便你在不需要它定时执行的时候清除它。1
2
3
4
5
6const id = setTimeout(() => {
// should run after 2 seconds
}, 2000)
// I changed my mind
clearTimeout(id)
Zero delay
如果把timeout指定为0,那么程序会尽可能快的执行callback,并且在当前函数执行之后。1
2
3
4
5
6setTimeout(() => {
console.log('after ')
}, 0)
console.log(' before ')
// 输出: before after
This is especially useful to avoid blocking the CPU on intensive tasks and let other functions be executed while performing a heavy calculation, by queuing functions in the scheduler.
setInterval(callback, interval)
setInterval和setTimeout类似,不同的是setTimeout只执行一次结束了,而setInterval会以一定的间隔不停的执行callback。1
2
3setInterval(() => {
// run every 2 seconds
}, 2000)
上面这个方法会每2秒执行一次callback,除非你告诉它停止运行,通过setInterval返回的timer id。
1 | const id = setInterval(() => { |
Note: 可以在callback内部执行clearInterval方法,来停止定时函数的执行。
setImmediate
相当于setTimeout(callback, 0),多用于node.js事件循环里
Recursive setTimeout(递归)
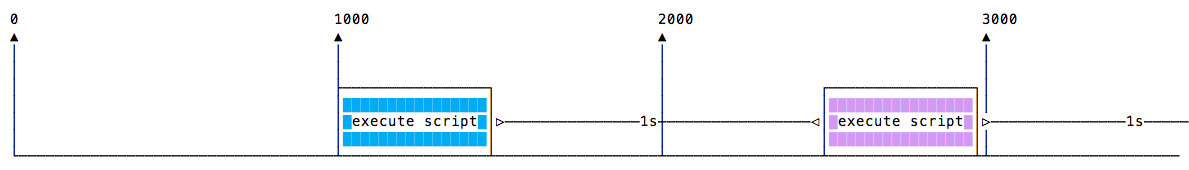
setInterval每n毫秒启动一个函数,不考虑函数何时完成执行。
如果每个方法都执行相同的时间,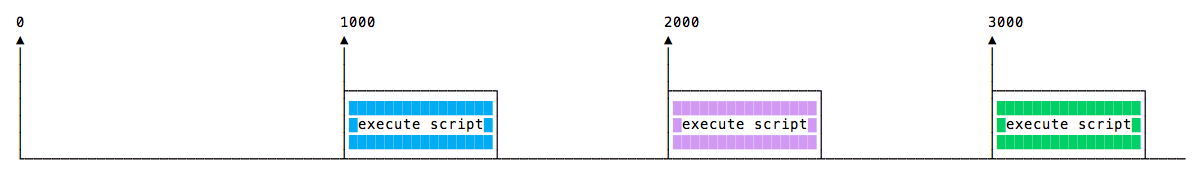
也有可能方法执行的时间依赖于网络等情况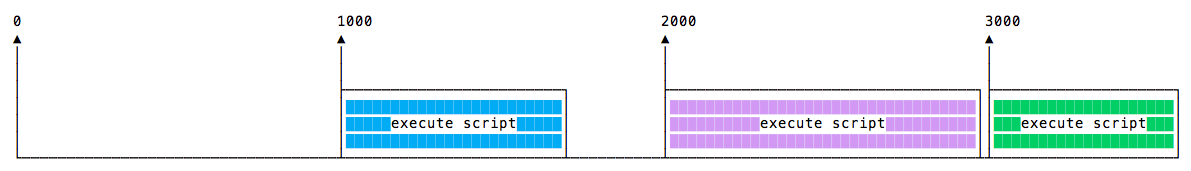
也有可能上一个方法执行的时间和下一个方法执行的时间重叠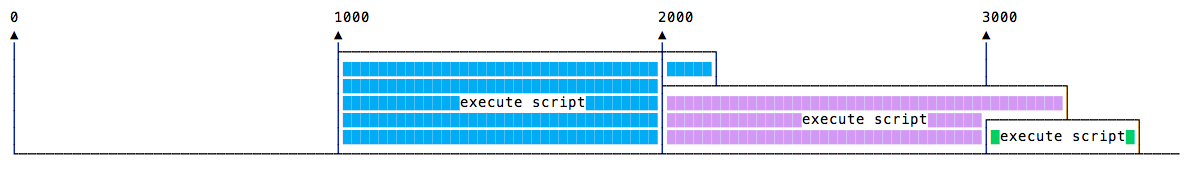
为了避免上面这种情况,你可以用递归setTimeout的形式来执行方法,效果如下: